如何实现定时推送?
一、概要
在工作当中遇到了一个需要定时向客户端推送新闻、文章等内容。这个时候在网上搜了很久没有找到合适的解决方案,其实能解决这个问题的方案有很多比如说用到一些大厂贡献的xxMQ中间件之类的,确实能解决问题。但是目前项目比较小根本用不上这么重的框架,在偶然的看到了一位大佬写的文章提供了一个非常不错的思路本篇文章也是受到他的启发实现了之后这里分享给大家。这个大佬的是58的沈剑文章名称是“1分钟实现延迟消息功能”。
关注本公众号回复“定时推送”即可获得源码地址
原文地址:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/eDMV25YqCPYjxQG-dvqSqQ
二、详细内容
详细内容大概分为4个部分,1.应用场景 2.遇到问题 3.设计 4.实现 5.运行效果
1.应用场景
需要定时推送数据,且轻量化的实现。
2.遇到问题
- 如果启动一个定时器去定时轮询
- (1)轮询效率比较低
- (2)每次扫库,已经被执行过记录,仍然会被扫描(只是不会出现在结果集中),会做重复工作
- (3)时效性不够好,如果每小时轮询一次,最差的情况下会有时间误差
- 如何利用“延时消息”,对于每个任务只触发一次,保证效率的同时保证实时性,是今天要讨论的问题。
3.设计
高效延时消息,包含两个重要的数据结构:
(1)环形队列,例如可以创建一个包含3600个slot的环形队列(本质是个数组)
(2)任务集合,环上每一个slot是一个Set
同时,启动一个timer,这个timer每隔1s,在上述环形队列中移动一格,有一个Current Index指针来标识正在检测的slot。
Task结构中有两个很重要的属性:
(1)Cycle-Num:当Current Index第几圈扫描到这个Slot时,执行任务
(2)Task-Function:需要执行的任务指针
假设当前Current Index指向第一格,当有延时消息到达之后,例如希望3610秒之后,触发一个延时消息任务,只需:
(1)计算这个Task应该放在哪一个slot,现在指向1,3610秒之后,应该是第11格,所以这个Task应该放在第11个slot的Set中
(2)计算这个Task的Cycle-Num,由于环形队列是3600格(每秒移动一格,正好1小时),这个任务是3610秒后执行,所以应该绕3610/3600=1圈之后再执行,于是Cycle-Num=1
Current Index不停的移动,每秒移动到一个新slot,这个slot中对应的Set,每个Task看Cycle-Num是不是0:
(1)如果不是0,说明还需要多移动几圈,将Cycle-Num减1
(2)如果是0,说明马上要执行这个Task了,取出Task-Funciton执行(可以用单独的线程来执行Task),并把这个Task从Set中删除
使用了“延时消息”方案之后,“订单48小时后关闭评价”的需求,只需将在订单关闭时,触发一个48小时之后的延时消息即可:
(1)无需再轮询全部订单,效率高
(2)一个订单,任务只执行一次
(3)时效性好,精确到秒(控制timer移动频率可以控制精度)
4.实现
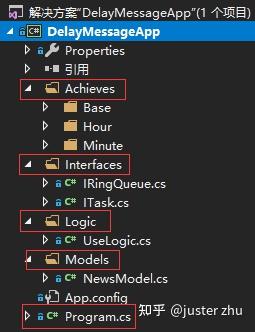
首先写一个方案要理清楚自己的项目结构,我做了如下分层。
Interfaces , 这层里主要约束延迟消息队列的队列和消息任务行。
public interface IRingQueue<T>{ /// <summary> /// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles] /// </summary> /// <param name="delayTime">The specified task is executed after N seconds.</param> /// <param name="action">Definitions of callback</param> void Add(long delayTime,Action<T> action); /// <summary> /// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles] /// </summary> /// <param name="delayTime">The specified task is executed after N seconds.</param> /// <param name="action">Definitions of callback.</param> /// <param name="data">Parameters used in the callback function.</param> void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data); /// <summary> /// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles] /// </summary> /// <param name="delayTime"></param> /// <param name="action">Definitions of callback</param> /// <param name="data">Parameters used in the callback function.</param> /// <param name="id">Task ID, used when deleting tasks.</param> void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data, long id); /// <summary> /// Remove tasks [need to know: where the task is, which specific task]. /// </summary> /// <param name="index">Task slot location</param> /// <param name="id">Task ID, used when deleting tasks.</param> void Remove(long id); /// <summary> /// Launch queue. /// </summary> void Start();} public interface ITask { }
Achieves,这层里实现之前定义的接口,这里写成抽象类是为了后面方便扩展。
using System;using System.Collections.Concurrent;using System.Linq;using System.Threading;using System.Threading.Tasks;using DelayMessageApp.Interfaces;namespace DelayMessageApp.Achieves.Base{public abstract class BaseQueue<T> : IRingQueue<T>{ private long _pointer = 0L; private ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[] _arraySlot; private int ArrayMax; /// <summary> /// Ring queue. /// </summary> public ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[] ArraySlot { get { return _arraySlot ?? (_arraySlot = new ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[ArrayMax]); } } public BaseQueue(int arrayMax) { if (arrayMax < 60 && arrayMax % 60 == 0) throw new Exception("Ring queue length cannot be less than 60 and is a multiple of 60 ."); ArrayMax = arrayMax; } public void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action) { Add(delayTime, action, default(T)); } public void Add(long delayTime,Action<T> action,T data) { Add(delayTime, action, data,0); } public void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data,long id) { NextSlot(delayTime, out long cycle, out long pointer); ArraySlot[pointer] = ArraySlot[pointer] ?? (ArraySlot[pointer] = new ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>()); var baseTask = new BaseTask<T>(cycle, action, data,id); ArraySlot[pointer].Add(baseTask); } /// <summary> /// Remove tasks based on ID. /// </summary> /// <param name="id"></param> public void Remove(long id) { try { Parallel.ForEach(ArraySlot, (ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>> collection, ParallelLoopState state) => { var resulTask = collection.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id); if (resulTask != null) { collection.TryTake(out resulTask); state.Break(); } }); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); } } public void Start() { while (true) { RightMovePointer(); Thread.Sleep(1000); Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString()); } } /// <summary> /// Calculate the information of the next slot. /// </summary> /// <param name="delayTime">Delayed execution time.</param> /// <param name="cycle">Number of turns.</param> /// <param name="index">Task location.</param> private void NextSlot(long delayTime, out long cycle,out long index) { try { var circle = delayTime / ArrayMax; var second = delayTime % ArrayMax; var current_pointer = GetPointer(); var queue_index = 0L; if (delayTime - ArrayMax > ArrayMax) { circle = 1; } else if (second > ArrayMax) { circle += 1; } if (delayTime - circle * ArrayMax < ArrayMax) { second = delayTime - circle * ArrayMax; } if (current_pointer + delayTime >= ArrayMax) { cycle = (int)((current_pointer + delayTime) / ArrayMax); if (current_pointer + second - ArrayMax < 0) { queue_index = current_pointer + second; } else if (current_pointer + second - ArrayMax > 0) { queue_index = current_pointer + second - ArrayMax; } } else { cycle = 0; queue_index = current_pointer + second; } index = queue_index; } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); throw; } } /// <summary> /// Get the current location of the pointer. /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> private long GetPointer() { return Interlocked.Read(ref _pointer); } /// <summary> /// Reset pointer position. /// </summary> private void ReSetPointer() { Interlocked.Exchange(ref _pointer, 0); } /// <summary> /// Pointer moves clockwise. /// </summary> private void RightMovePointer() { try { if (GetPointer() >= ArrayMax - 1) { ReSetPointer(); } else { Interlocked.Increment(ref _pointer); } var pointer = GetPointer(); var taskCollection = ArraySlot[pointer]; if (taskCollection == null || taskCollection.Count == 0) return; Parallel.ForEach(taskCollection, (BaseTask<T> task) => { if (task.Cycle > 0) { task.SubCycleNumber(); } if (task.Cycle <= 0) { taskCollection.TryTake(out task); task.TaskAction(task.Data); } }); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine(e); throw; } }}}using System;using System.Threading;using DelayMessageApp.Interfaces;namespace DelayMessageApp.Achieves.Base{public class BaseTask<T> : ITask{ private long _cycle; private long _id; private T _data; public Action<T> TaskAction { get; set; } public long Cycle { get { return Interlocked.Read(ref _cycle); } set { Interlocked.Exchange(ref _cycle, value); } } public long Id { get { return _id; } set { _id = value; } } public T Data { get { return _data; } set { _data = value; } } public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action, T data,long id) { Cycle = cycle; TaskAction = action; Data = data; Id = id; } public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action,T data) { Cycle = cycle; TaskAction = action; Data = data; } public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action) { Cycle = cycle; TaskAction = action; } public void SubCycleNumber() { Interlocked.Decrement(ref _cycle); }}}
Logic,这层主要实现调用逻辑,调用者最终只需要关心把任务放进队列并指定什么时候执行就行了,根本不需要关心其它的任何信息。
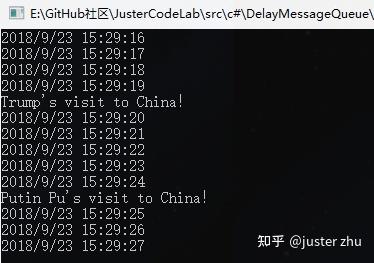
public static void Start(){ //1.Initialize queues of different granularity. IRingQueue<NewsModel> minuteRingQueue = new MinuteQueue<NewsModel>(); //2.Open thread. var lstTasks = new List<Task> { Task.Factory.StartNew(minuteRingQueue.Start) }; //3.Add tasks performed in different periods. minuteRingQueue.Add(5, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) => { Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News); }), new NewsModel() { News = "Trump's visit to China!" }); minuteRingQueue.Add(10, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) => { Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News); }), new NewsModel() { News = "Putin Pu's visit to China!" }); minuteRingQueue.Add(60, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) => { Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News); }), new NewsModel() { News = "Eisenhower's visit to China!" }); minuteRingQueue.Add(120, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) => { Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News); }), new NewsModel() { News = "Xi Jinping's visit to the US!" }); //3.Waiting for all tasks to complete is usually not completed. Because there is an infinite loop. //F5 Run the program and see the effect. Task.WaitAll(lstTasks.ToArray()); Console.Read();}
Models,这层就是用来在延迟任务中带入的数据模型类而已了。自己用的时候换成任意自定义类型都可以。